Dimension Reduction
Background
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is a rapidly growing and widely applying technology. By measuring gene expression at a single-cell level, scRNA-seq provides an unprecedented opportunity to investigate the cellular heterogeneity of complex tissues. However, despite the popularity of scRNA-seq, analyzing scRNA-seq data remains a challenging task. Specifically, due to the low capture efficiency and low sequencing depth per cell in scRNA-seq data, gene expression measurements obtained from scRNA-seq are noisy: collected scRNA-seq gene measurements are often in the form of low expression counts, and in studies not based on unique molecular identifiers, are also paired with an excessive number of zeros known as dropouts. Subsequently, dimensionality reduction methods that transform the original high-dimensional noisy expression matrix into a low-dimensional subspace with enriched signals become an important data processing step for scRNA-seq analysis. Proper dimensionality reduction can allow for effective noise removal, facilitate data visualization, and enable efficient and effective downstream analysis of scRNA-seq. Dimensionality reduction is indispensable for many types of scRNA-seq analysis. Unfortunately, despite the critical importance of DR in scRNAseq analysis and the vast number of DR methods developed for scRNAseq studies, however, few comprehensive comparison studies have been performed to evaluate the effectiveness of different DR methods in scRNAseq.
Overview of our study
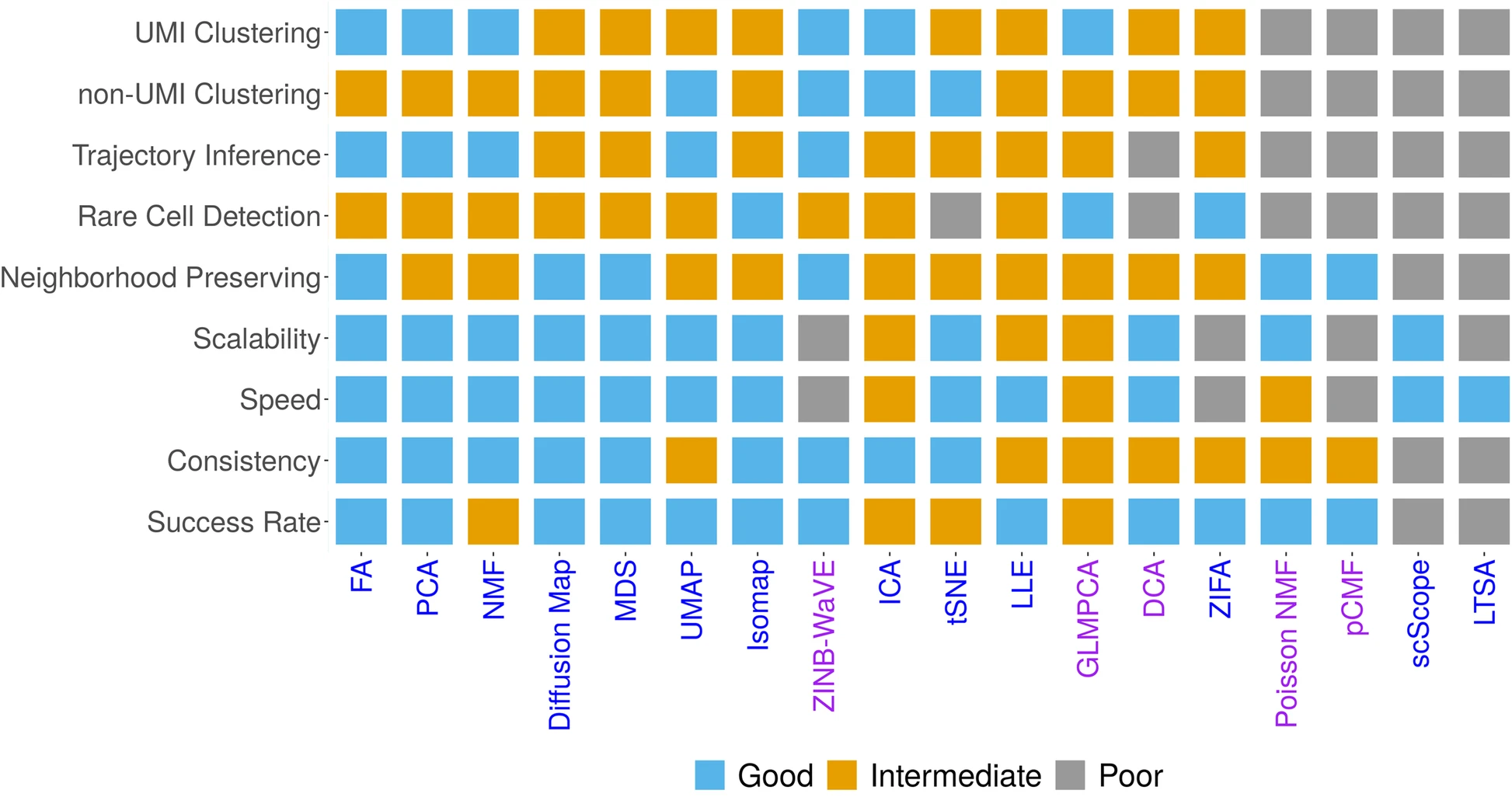
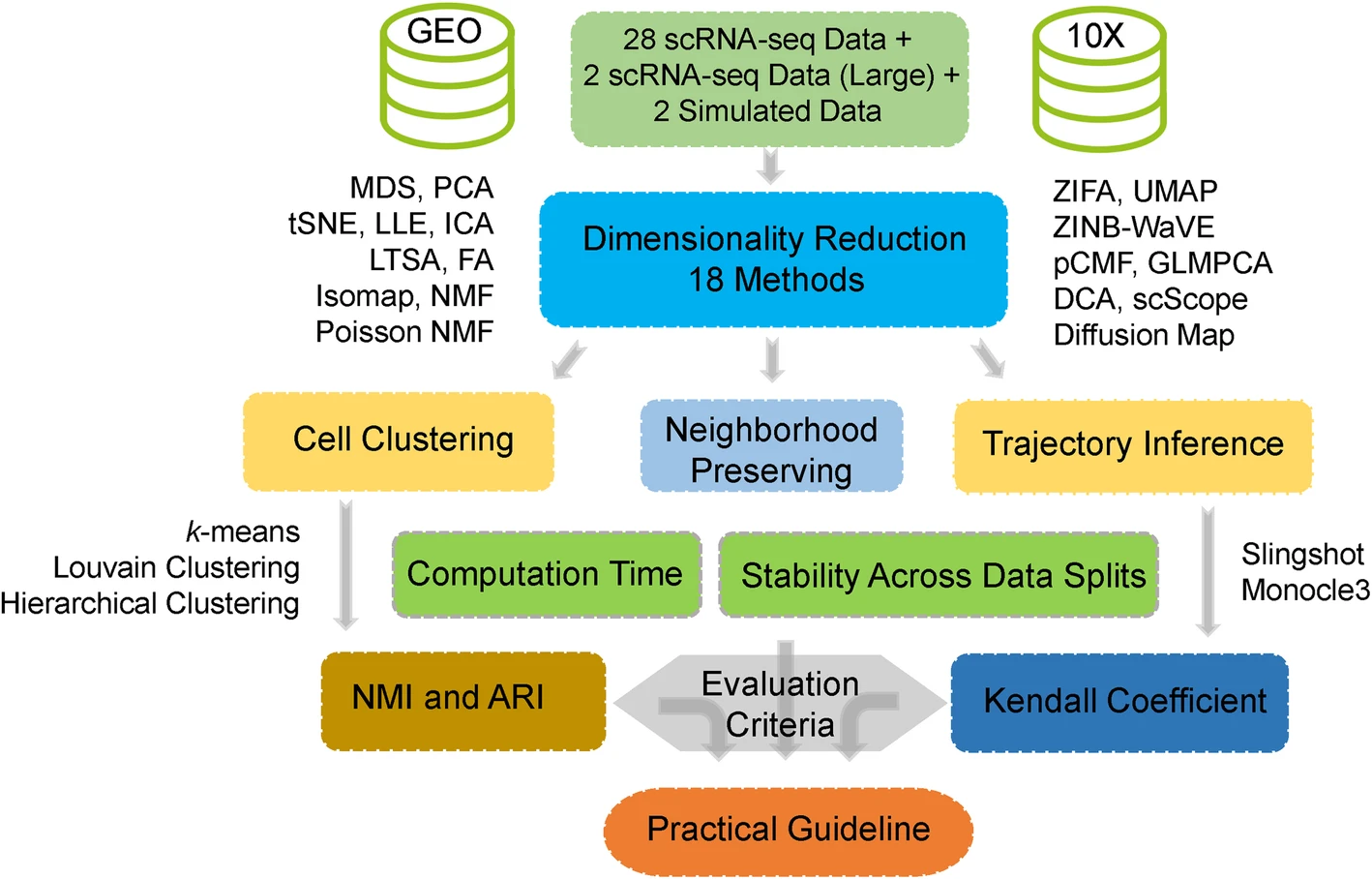
Here, we aim to fill this critical knowledge gap by providing a comprehensive comparative evaluation of a variety of commonly used dimensionality reduction methods for scRNA-seq studies. Specifically, we compared 18 different dimensionality reduction methods on 30 publicly available scRNA-seq data sets that cover a range of sequencing techniques and sample sizes. We evaluated the performance of different dimensionality reduction methods for neighborhood preserving in terms of their ability to recover features of the original expression matrix, and for cell clustering and lineage reconstruction in terms of their accuracy and robustness using different metrics. We also evaluated the computational scalability of different dimensionality reduction methods by recording their computational time. Together, we hope our results can serve as an important guideline for practitioners to choose dimensionality reduction methods in the field of scRNA-seq analysis.
Paper
Accuracy, robustness and scalability of dimensionality reduction methods for single-cell RNA-seq analysis
Paper Published in Genome Biology
Selected important results
ased on the comprehensive evaluation results, we provide important guidelines for choosing DR methods for scRNAseq data analysis. We also provide all analysis scripts used in the present study at [http://xzlab.org/reproduce.html](http://xzlab.org/reproduce.html).Together, we hope that our results will serve as an important practical reference for practitioners to choose DR methods in the field of scRNAseq analysis.