iDEA
Background
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is becoming a standard technique for transcriptome profiling and is widely applied to many areas of genomics. Compared to the previous bulk RNAseq technique that measures the average gene expression of a potentially heterogeneous cell population, scRNA-seq is capable of producing gene expression measurements both at the genome-wide scale and at a single-cell resolution1. Because of the technical advantages, various scRNA-seq studies are being performed to reveal complex cellular heterogeneity in tissues, yielding important insights into many biological processes. However, due to the low amount of mRNAs available in a single cell and the low capture efficiency in the sequencing technique, scRNA-seq data are often extremely noisy2. Effective analysis of noisy scRNA-seq data requires development of powerful statistical tools. Here, we develop such a tool for two of the most commonly applied analysis in scRNA-seq studies: differential expression (DE) analysis and gene set enrichment (GSE) analysis.
Overview of iDEA
To increase the power of both DE and GSE analysis and ensure result reproducibility for scRNA-seq analysis, we developed a statistical method, which we refer to as the integrative Differential expression and gene set Enrichment Analysis (iDEA), that addresses the aforementioned shortcomings of previous methods for scRNA-seq data analysis. iDEA models all genes together by borrowing information across genes in terms of DE effect size distributional properties. iDEA also integrates DE analysis and GSE analysis into a joint statistical framework, providing substantial power gains for both analytic tasks. Importantly, iDEA makes use of summary statistics output from existing DE tools and does not make explicit modeling assumptions on the individual-level scRNA-seq data. Use of summary statistics not only allows iDEA to take advantage of various existing DE models for effective and flexible data modeling, but also ensures its scalable computation to large-scale scRNA-seq data sets. In addition, incorporating summary statistics from scRNA-seq DE analysis into GSE analysis under the framework of iDEA makes GSE analysis less susceptible to gene-gene correlations and other technical difficulties such as dropout events. We illustrate the benefits of iDEA with extensive simulations and applications to three scRNA-seq data.
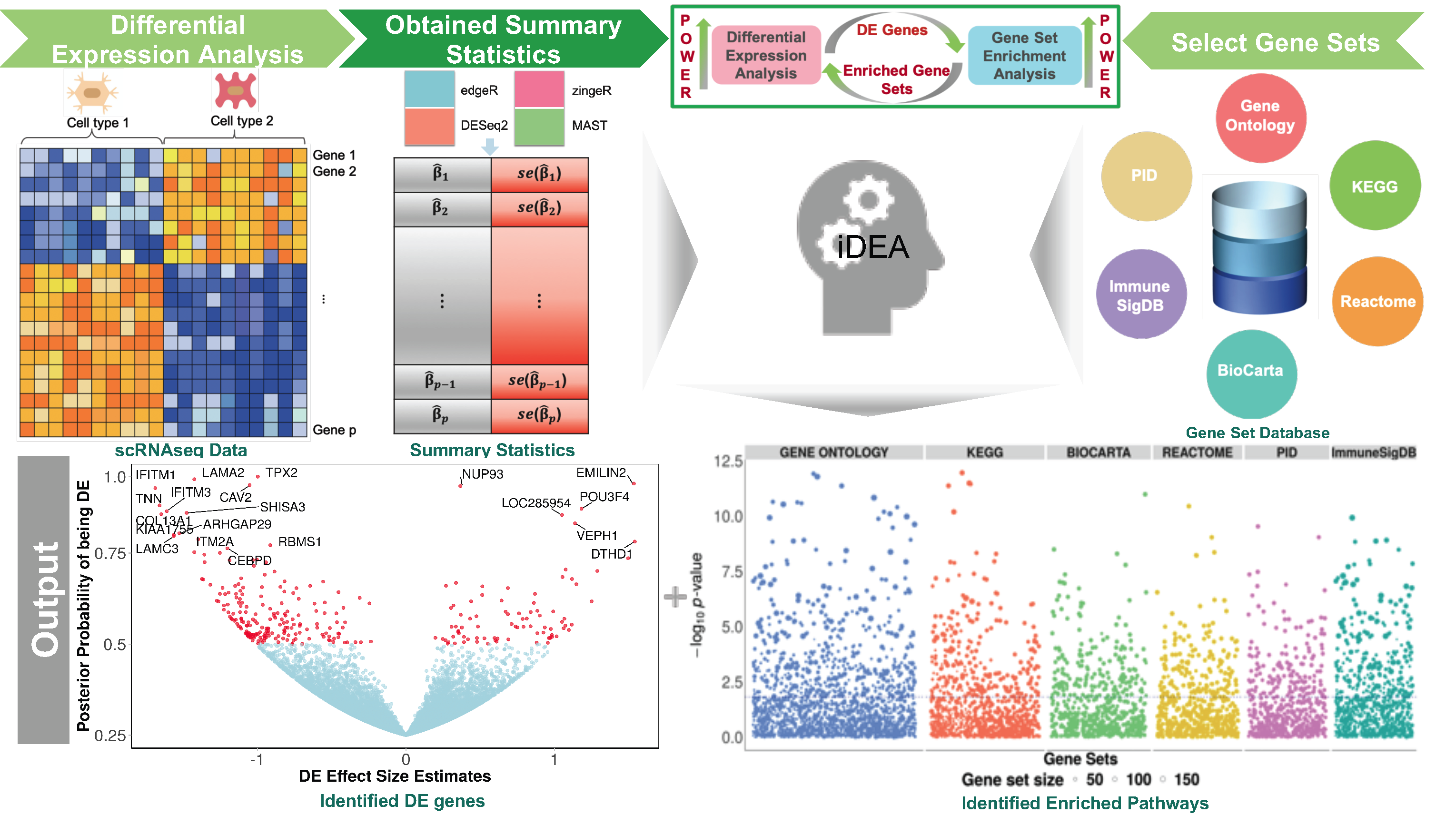
Paper
Integrative differential expression and gene set enrichment analysis using summary statistics for scRNA-seq studies
Paper Published in Nature Communications
Selected important results by iDEA
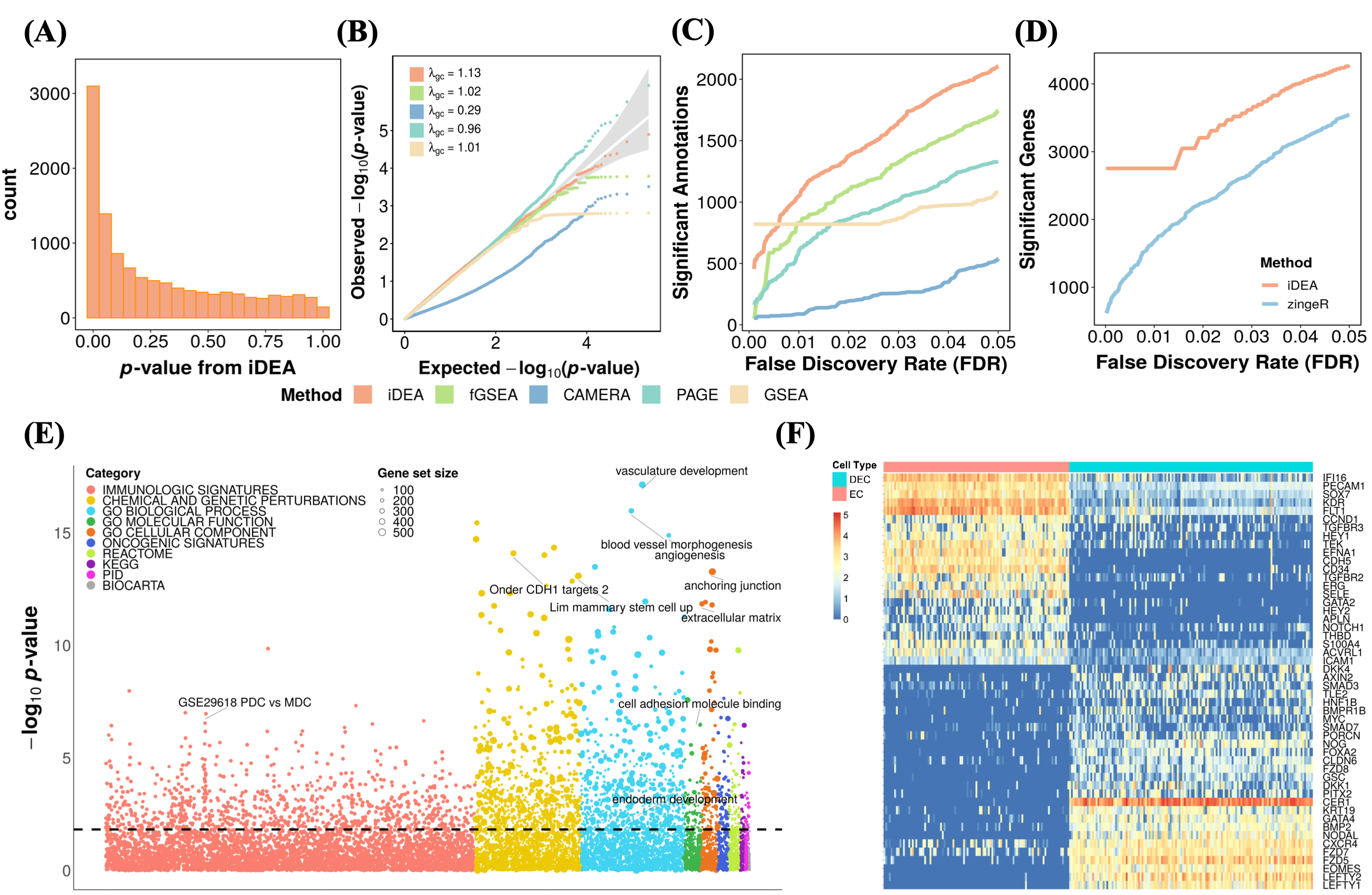
Analyzing the human embryonic stem cell scRNA-seq data, iDEA produces calibrated p-values , identified more significantly enriched gene sets compared to the other GSE methods. Notably, besides the statistical power, many of the top gene sets identified by iDEA are closely related to embryonic developmen. Examples include the Wnt signaling pathway, the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) receptor signaling pathway30, and relevant GO terms such as GO:0048514 (blood vessel morphogenesis), GO:0001944 (vasculature development) and GO:0007492 (endoderm development). Furthermore, iDEA identifies more DE genes than existing methods, while the top 50 selected important DE genes identified by iDEA clearly distinguishes the two examined cell types, DEC and EC cells.
Tutorial of iDEA
We provided a tutorial for running iDEA in details, with detailed interpretation of the results. Package Website: iDEA Tutorial
